
[ad_1]
- The US dollar remains on the back foot for the second day in a row, although it lacks the follow -up sale.
- Technical preparation is preferred to decrease and supports the risk of a decrease in a decrease.
- A continuous break under SMA 200 periods on H4 to reaffirm negative expectations.
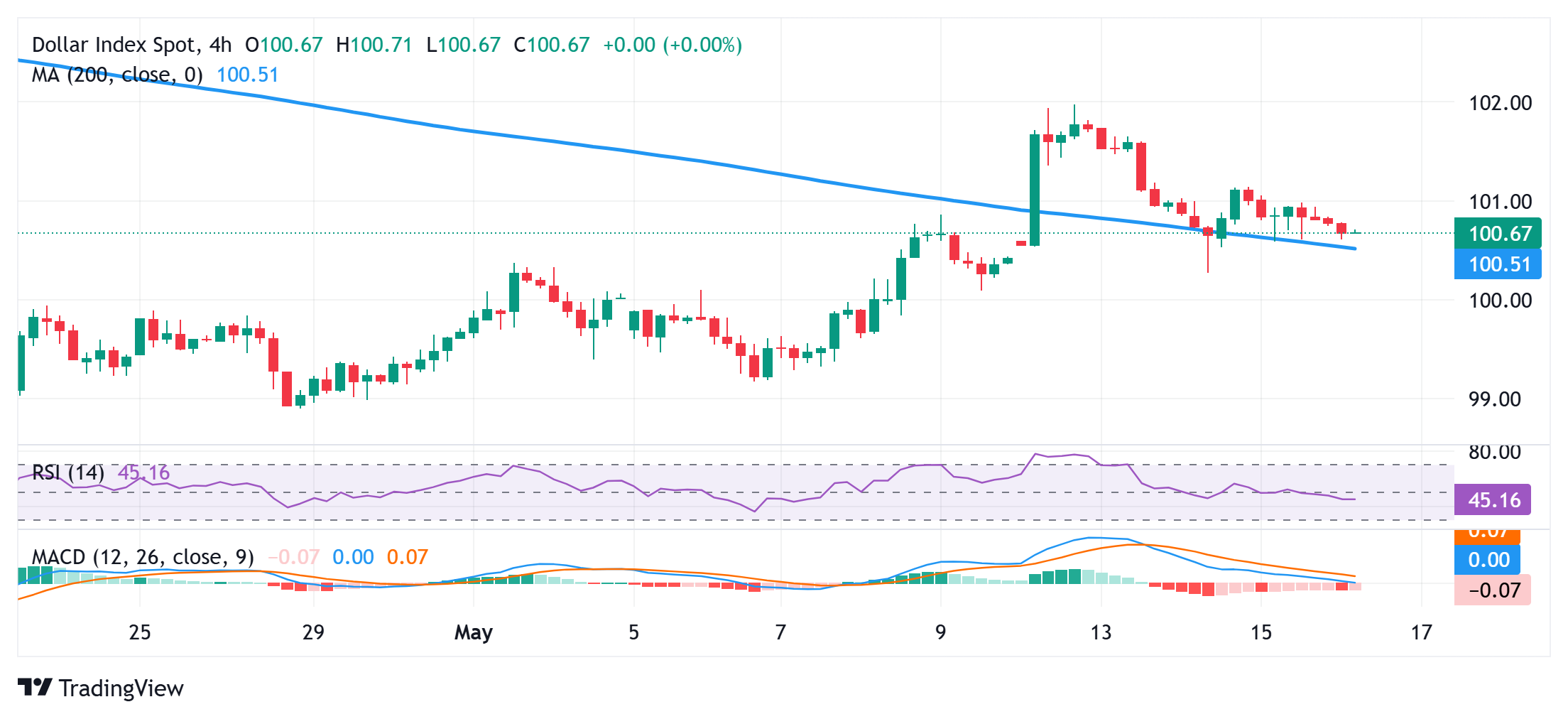
The US dollar index (DXY), which tracks Greenback against a basket of currencies, is trading with a negative bias for the second day in a row on Friday, although the fall inside the day lacks the Habbudian condemnation. The index is currently trading around the area of 100.70, a slightly more than 0.10 % decrease for this day, and it can stick to more than 200 moving averages (SMA) on the graph for 4 hours.
Meanwhile, the technical indicators support the graphs every day/daily horizons of collapse without the aforementioned support, currently related to the 100.50 region. The subsequent DXY falls can make a vulnerable to extend the decline slide this week from its highest levels since April 10 and the low weekly swing test, about 100.00 psychological marks touched on Wednesday.
Some of the followers will indicate that the recent recovery from Loun Touged on April 21 runs its course and paves the way for deeper losses. DXY can decrease to the intermediate support 99.60-99.55 on its way to the 99.20 area and the 99.00 ring brand.
On the other hand, the immediate obstacle is linked near the 101.00-101.10 area, which can raise the fresh match from a short-range step to the 101.70 region. The bulls in US dollar (USD) may then try to overcome the 102.00 brand. The ongoing power that exceeds the latter may deny any negative bias in the short term and pave the way for some important move.
DXY 4 hours graph
Questions and answers in US dollars
The USD (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and a “reality” currency for a large number of other countries where there is a circulating alongside local notes. It is the most trading currency in the world, as it represents more than 88 % of the rotation of global foreign currencies, or on average $ 6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. In the aftermath of World War II, the United States took over the British pound the world reserves. For most of its history, the US dollar was backed by gold, even the Bretton Woods agreement in 1971 when the golden standard went.
The most important individual factor that affects the value of the US dollar is the monetary policy, which is formed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Federal Reserve has two states: to achieve price stability (control of control) and enhance full employment. Its primary performance to achieve these two goals is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise very quickly and inflation is 2 % higher than the Federal Reserve goal, the Federal Reserve will raise rates, which helps the value of the dollar. When inflation decreases to less than 2 % or the unemployment rate is very high, the Federal Reserve may reduce interest rates, which weighs to green.
In maximum situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and quantitative mitigation (QE). QE is the process that the Federal Reserve increases significantly from the flow of credit in a suspended financial system. It is a measure of the non -standard policy used when the credit is dry because banks will not lend to each other (for fear of failing to pay the opposite end). It is the last resort when it is unlikely to achieve interest rates simply the necessary result. The Federal Reserve is the preferred to combat the credit crisis that occurred during the great financial crisis in 2008. It includes the printing of the Federal Reserve more dollars and their use to buy US government bonds mostly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to the weakest US dollar.
The quantitative tightening (QT) is the opposite process in which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not invest the manager from the bonds he holds in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
